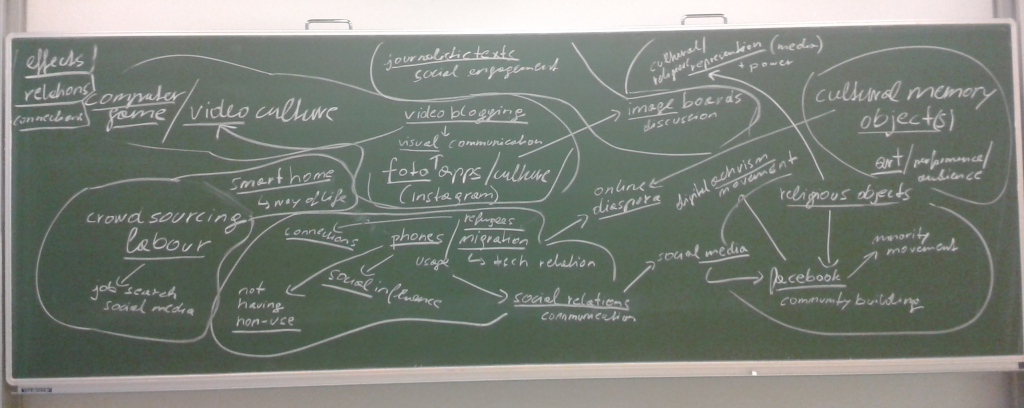
Clustering of individual ideas to create joint research projects in the seminar “Media and Visual Technologies as Material Culture” at the Department of Social and Cultural Anthropology of the University of Vienna.
Posts tagged technology
Seminar: Media & visual technologies as material culture – course description
Seminar “Media and visual technologies as material culture” by Philipp Budka
MA Program CREOLE & MA Program Social & Cultural Anthropology
University of Vienna
Seminar Description
This course gives an overview about material culture as conceptual approach to understand media and visual technologies. It focuses on digital media technologies, their visual aspects and how they are integrated and practiced in everyday life.
Continue reading Seminar: Media & visual technologies as material culture – course description
Article: From marginalization to self-determined participation
Budka, P. 2015. From marginalization to self-determined participation: Indigenous digital infrastructures and technology appropriation in Northwestern Ontario’s remote communities. Journal des Anthropologues – Special Issue “Margins and Digital Technologies”. No. 142-143: 127-153.
Abstract
This article discusses, from an anthropological perspective, the utilization of digital infrastructures and technologies in the geographical and sociocultural contexts of indigenous Northwestern Ontario, Canada. By introducing the case of the Keewaytinook Okimakanak Kuh-ke-nah Network (KO-KNET) it analyses first how digital infrastructures not only connect First Nations people and communities but also enable relationships between local communities and non-indigenous institutions. Second, and by drawing on KO-KNET’s homepage service MyKnet.org, it exemplifies how people appropriate digital technologies for their specific needs in a remote and isolated area. KO-KNET and its services facilitate First Nations’ self-determined participation to regional, national, and even global ICT connectivity processes, contributing thus to the “digital demarginalization” of Northwestern Ontario’s remote communities.
Vortrag: Indigene Modernität durch digitale Medientechnologien?
Budka, P. 2015. Indigene Modernität durch digitale Medientechnologien? Infrastrukturentwicklung, Technologieaneignung und soziokulturelle Praktiken im Nordwestlichen Ontario, Kanada. Vortrag im Colloquium Americanum des Instituts für Ethnologie der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt, 25. Juni 2015. (PDF)
Inhalt:
Einleitung
„Modernität“ & Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie/Ethnologie
„Indigenisierte Modernität“
Indigene & Digitale Medientechnologien
Internetinfrastruktur im Nordwestlichen Ontario, Kanada
Soziale (sozial-digitale) Praktiken
„Indigene Modernität“ durch digitale Medientechnologien?
Paper: Von „Cyber Anthropologie“ zu „Digitaler Anthropologie“: kultur- und sozialanthropologische Beiträge zur Erforschung digitaler Medientechnologien.
Budka. P. 2014. Von „Cyber Anthropologie“ zu „Digitaler Anthropologie“: kultur- und sozialanthropologische Beiträge zur Erforschung digitaler Medientechnologien. Vortrag im Rahmen der Ringvorlesung: „Rituale, Medien, Bewusstsein – in Memoriam Manfred Kremser“, 9. Januar 2014.
Einleitung
Dieser Vortrag wirft einen Blick auf die kultur- und sozialanthropologische Erforschung digitaler Medientechnologien wie Internet, Soziale Online-Netzwerke und mobile Kommunikationstechnologien. Dabei werden die Grundzüge des Forschungsfeldes der „Cyber Anthropologie“ – besonders im Bezug zum Wiener Institut für Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie – ebenso vorgestellt wie die rezente Entwicklung einer „Digitalen Anthropologie“. Die gemeinsame, übergeordnete Frage dieser kultur- und sozialanthropologischen Projekte lautet: „Was bedeutet Menschsein in einer (zunehmend) digitalen Welt?“. Fallbeispiele aus der ethnographischen Forschungspraxis behandeln konkrete Aspekte des „digitalen Menschseins“ und runden die theoretische Diskussion ab.
Medienanthropologie und die technische Mediatisierung von Kommunikation
In der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie lässt sich die Forschung zu Medientechnologien grundsätzlich als Forschung zu menschlicher Kommunikation, die von Technologien mediatisiert wird, verstehen. Diese Mediatisierung von Kommunikation ist für die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie besonders hinsichtlich ihrer Einbettung in soziokulturelle und historische Prozesse und Kontexte interessant: „The key questions for the anthropologist are how these technologies operate to mediate human communication, and how such mediation is embedded in broader social and historical processes“ (Peterson 2003: 5).
In der Medienanthropologie geht es um die Mediatisierung von Kommunikation in unterschiedlichen soziokulturellen Kontexten und unter spezifischen historischen, politischen und ökonomischen Bedingungen.
In der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie werden Medien nicht auf ihre Inhalte oder Botschaften reduziert. Im Versuch ein möglichst ganzheitliches Bild von Medienphänomenen zu erlangen, werden Kontexte und Bedingungen unter denen Medien produziert, verteilt und genutzt werden ebenso analysiert wie die technischen Aspekte von Medien. Medien beinhalten immer auch Technologien, die die Mediatisierung von Kommunikation erst ermöglichen. Es macht also Sinn nicht nur von Medien sondern von Medientechnologien zu sprechen.
Über Medientechnologien entwickeln Menschen neue Beziehungen zu Zeit und Raum sowie zu Körper und Wahrnehmung. Und diese Verhältnisse verändern sich aufgrund medientechnologischer Entwicklungen permanent. Die „greifbare“ Materialität von Medientechnologien und die damit verbundenen phänomenologischen Erfahrungen sind also wesentlicher Gegenstand medienethnographischer und medienanthropologischer Forschung (vgl. Ginsburg et al. 2002: 21).
Wichtigste methodische Herangehensweise, um Medienphänomene zu erfassen, ist für die Medienanthropologie, wie für die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie im Allgemeinen, die ethnographische Feldforschung. Diese methodische Strategie zur empirischen Datenerhebung passt sich dabei sowohl dem Feld als auch den soziokulturellen Handlungsräumen der Menschen an (vgl. z.B. Kremser 1998, Marcus 1998) und kann sich also nicht allein auf Inhalte und deren Rezeption beschränken. Sie muss auch die physischen und sensorischen Dimensionen von Medientechnologien miteinbeziehen, weil über diese soziale Beziehungen hergestellt werden können.
Technologie im soziokulturellen Kontext
Seit den 1950er Jahren untersuchen Kultur- und SozialanthropologInnen neue und „moderne“ Technologien und wie diese vor allem in „nicht-westlichen“ Gemeinschaften verwendet und angeeignet werden (vgl. z.B. Beck 2001, Godelier 1971, Pfaffenberger 1992, Sharp 1952). Doch wie unter anderem Arturo Escobar (1994) meint, ist es schwierig diese Forschungsansätze und -befunde auf hochkomplexe technische Umgebungen in „modernen“ Gesellschaften zu übertragen. Aus kultur- und sozialanthropologischer Perspektive bedeutet diese Transferschwierigkeit weder eine Hierarchisierung von soziotechnischen Systemen und damit verbunden von Gesellschaften, noch bedeutet dies eine Abwertung „nicht-moderner“ oder „traditioneller“ soziotechnischer Systeme. All diese Systeme – vom Töpfern in Indien bis zum Programmieren von Software in Kalifornien – sind hochkomplex und heterogen.
Es besteht allerdings dringender Bedarf an theoretischen Zugängen und weiteren empirischen Befunden, die zum Verständnis soziotechnischer Systeme in „modernen“ Gesellschaften beitragen. So befasst sich auch die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie zunehmend mit soziotechnischen Systemen in zeitgenössischen Gesellschaften (vgl. z.B. Rabinow 2008, Rabinow & Marcus 2008) – vor allem auch, weil immer wieder Fragen auftauchen, die scheinbar nur von der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie beantwortet werden können, etwa nach der soziokulturellen und soziokulturell unterschiedlichen Bedeutung von Technologien (vgl. Pfaffenberger 1988, 1992).
Die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie versucht zu verstehen, wie Technologie – beispielsweise in Form materieller Kultur oder als soziotechnisches System – (kulturell) konstruiert und (sozial) verwendet, genutzt und angeeignet wird. Ähnliche Ziele verfolgen auch Wissenschaftsforschung, Science and Technology Studies und sozialwissenschaftliche Technikforschung (vgl. z.B. Eglash 2006). Die Entwicklung und der Aufschwung digitaler (Medien)Technologien führen zu einer weiteren Differenzierung dieses Forschungsbereichs und zur Etablierung neuer Schwerpunkte.
Article: Digitale Medientechnologien aus kultur- und sozialanthropologischer Perspektive
Budka, P. 2013. Digitale Medientechnologien aus kultur- und sozialanthropologischer Perspektive: Überlegungen zu Technologie als materielle Kultur und Fetisch (Digital media technologies from an anthropological perspective: Reflections on technology as material culture and fetish). Medien und Zeit, 28, 1/2013: 22-34.
Abstract
Dieser Aufsatz blickt auf digitale Medientechnologien aus Perspektive der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie. In einem wissenschaftstheoretischen und historischen Abriss werden einerseits Eckpunkte in der Entwicklung relevanter Forschungsfelder, wie die Anthropologie und Ethnographie der Medientechnologien, die Digitale Anthropologie sowie die Anthropologie der Cyberkultur behandelt. Andererseits werden zwei Fallbeispiele aus der ethnographischen Forschungspraxis vorgestellt, die digitale Technologien als materielle Kultur verstehen. Technologie als materielle Kultur erlaubt es die Materialität und die Normativität von Technologien ebenso zu fassen wie deren alltägliche Aneignung in wandelnden soziokulturellen, politischen und ökonomischen Kontexten. Der Aufsatz schließt mit einer Diskussion der Fetischisierung von Technologien, deren Bedeutung und Zusammenhänge.
Word cloud on identity, sociality, communality & digital media technologies
Word cloud of the student projects in the seminar “Identity, sociality & communality in times of digital media technologies” at the Department of Social and Cultural Anthropology, University of Vienna.
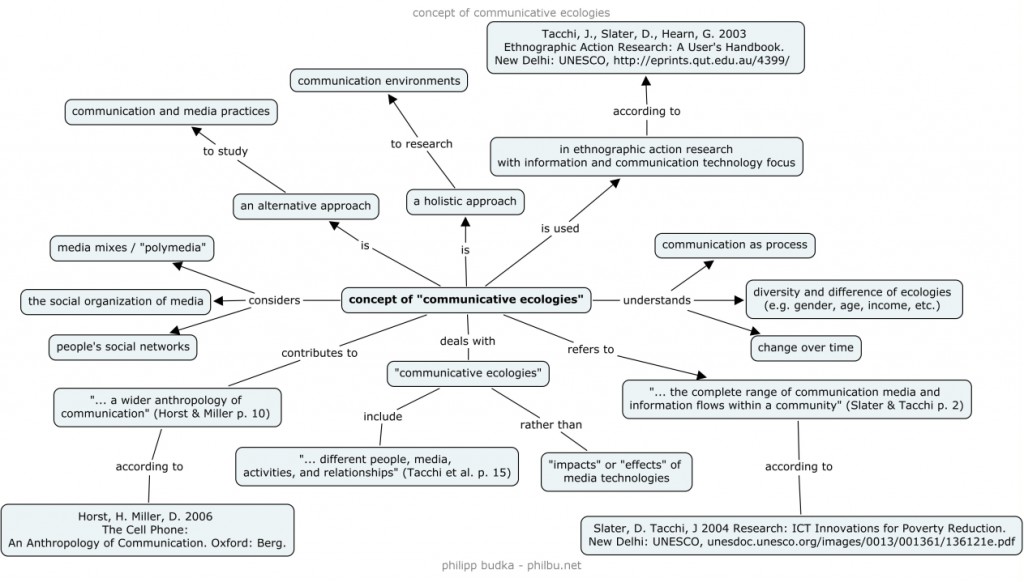
Concept map: Communicative ecologies
This map visualizes the concept of “communicative ecologies” as introduced by Tacchi, J., Slater, D., Hearn, G. 2003. Ethnographic Action Research: A User’s Handbook. New Delhi: UNESCO, http://eprints.qut.edu.au/4399/. It was done by using the free CMap Tools (click to enlarge).
Free e-Book: Connecting Canadians: Investigations in Community Informatics
A. Clement, M. Gurstein, G. Longford, M. Moll & L. R. Shade (Eds.), Connecting Canadians: Investigations in Community Informatics. Edmonton: Athabasca University Press.
“Connecting Canadians represents the work of the Community Research Alliance for Community Innovation and Networking (CRACIN), the largest national and international research effort to examine the burgeoning field of community informatics, a cross-disciplinary approach to the mobilization of information and communications technologies (ICT) for community change.
Funded for four years by the SSHRC’s Initiative for the New Economy, CRACIN systematically studied a wide variety of Canadian community ICT initiatives, bringing perspectives from sociology, computer science, critical theory, women’s studies, library and information sciences, and management studies to bear on networking technologies. A comprehensive thematic account of this in-depth research, Connecting Canadians will be an essential resource for NGOs, governments, the private sector, and multilateral agencies across the globe.”
Download the book or single chapters for free: http://www.aupress.ca/index.php/books/120193
Video on internet infrastructure by Ben Mendelsohn
Paper: Interactive technology enhanced learning for social science students
Budka, P., Schallert, C., Mader, E. “Interactive technology enhanced learning for social science students”, Paper for ICL Conference 2011, Piestany, Slovakia, 21-23 September 2011.
Abstract
This paper introduces the case of an interactive technology enhanced learning model, its contexts and infrastructure at a public university in the Bologna era. From a socio-technological perspective, it takes a look at the conditions and challenges under which this flexible learning model for the social sciences has been developed. Furthermore, selected evaluation results, including experiences and expectations of social science students, are discussed. The paper concludes that it is possible, with the appropriate didactical model, to create and facilitate interactive student-centered learning situations, even in “mass lectures”.
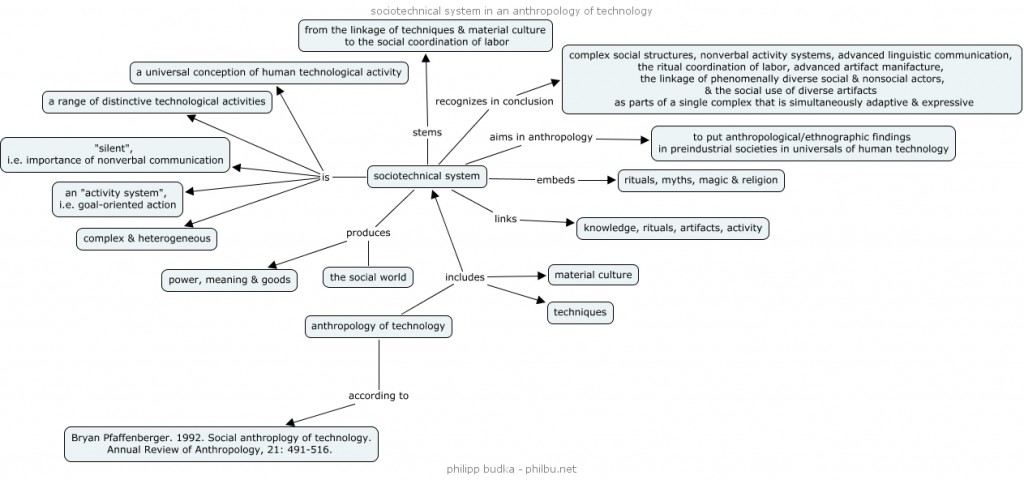
Concept map: Sociotechnical system in an anthropology of technology
This concept map builds on Bryan Pfaffenberger’s article “Social anthropology of technology”, Annual Review of Anthropology 21(1992), pp. 491-516, in which he discusses the use of sociotechnical systems in an anthropological context. This map tries to visualize the concept. It was done by using the free CMap Tools (click to enlarge).
Article: Lehren & Lernen mit Technologien an Hochschulen
Budka, P., Ebner, M., Nagler, W., Schallert, C. 2011. Hochschule – Strukturen, Rahmen und Modelle für die Lehre mit Technologien. In Ebner, M. & S. Schön (Eds.), Lehrbuch für Lernen und Lehren mit Technologien.
Abstract
Ausgehend von der bestehenden Bildungslandschaft und ihres politisch historischen Entwicklungskorsetts diskutiert dieser Beitrag das Potential von mit digitalen Medien und Technologien gestütztem Lehren und Lernen an Hochschulen. Unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von organisatorischen und infrastrukturellen Rahmenbedingungen und anhand des Spezialfalls der universitären Massenlehrveranstaltung werden ein didaktisches Modell sowie die Anwendungen von Lernmanagementsystemen vorgestellt. Dabei wird vor allem der Frage nachgegangen, wie Interaktion und Interaktivität in Lehrveranstaltungen mittels entsprechend didaktischer Modelle und mit Unterstützung von Lernsystemen gesteigert und verbessert werden können. Beispiele aus der Praxis und Maßnahmen für den Einsatz von digitalen Medientechnologien in der universitären Lehre ergänzen das Kapitel.
L3T – Lehrbuch für Lernen und Lehren mit Technologien
Mehr zu L3T
Article: Transforming learning infrastructures in the social sciences through flexible and interactive technology-enhanced learning
Budka, P., & Schallert, C. 2009. Transforming learning infrastructures in the social sciences through flexible and interactive technology-enhanced learning. In: Learning Inquiry, 3(3), 131-142.
Abstract
The changing higher educational landscape in Europe creates new learning infrastructures and transforms existing ones. Students are thus provided with new possibilities and challenges. Through the case study of a newly developed common curriculum for the social sciences of a public university in Austria, this article discusses the interacting social agents, elements, and tools of a flexible and interactive technology-enhanced learning model. In doing so, the transnational, national, and local infrastructural conditions and challenges are critically examined from a socio-technological perspective. Selected evaluation and survey results highlight students’ learning practices, usage behavior, and suggestions to improve their learning situation. The article concludes that student-centered learning models focusing on flexibility and interactivity can support the stable implementation of a common curriculum and its technology-enhanced learning infrastructure for the social sciences at public universities with high student numbers.
Keywords
Higher education – Learning – Infrastructure – Social sciences – Austria
Report: CRASSH Workshop “Subversion, Conversion, Development”
From the workshop’s abstract:
As part of the “New forms of knowledge for the 21st Century” research agenda at Cambridge University, the workshop will explore why designers and developers of new technologies should be interested in producing objects that users can modify, redeploy or redevelop. This exploration demands an examination of presuppositions that underpin the knowledge practices associated with the various productions of information communication technologies (ICT). A central question is that of diversity: diversity of use, of purpose, and of value(s). Does diversity matter, in the production and use of ICT, and if so, why?
Links:
http://www.crassh.cam.ac.uk/events/71/
http://vectors.usc.edu/thoughtmesh/publish/12.php