Budka. P. 2014. Von „Cyber Anthropologie“ zu „Digitaler Anthropologie“: kultur- und sozialanthropologische Beiträge zur Erforschung digitaler Medientechnologien. Vortrag im Rahmen der Ringvorlesung: „Rituale, Medien, Bewusstsein – in Memoriam Manfred Kremser“, 9. Januar 2014.
Einleitung
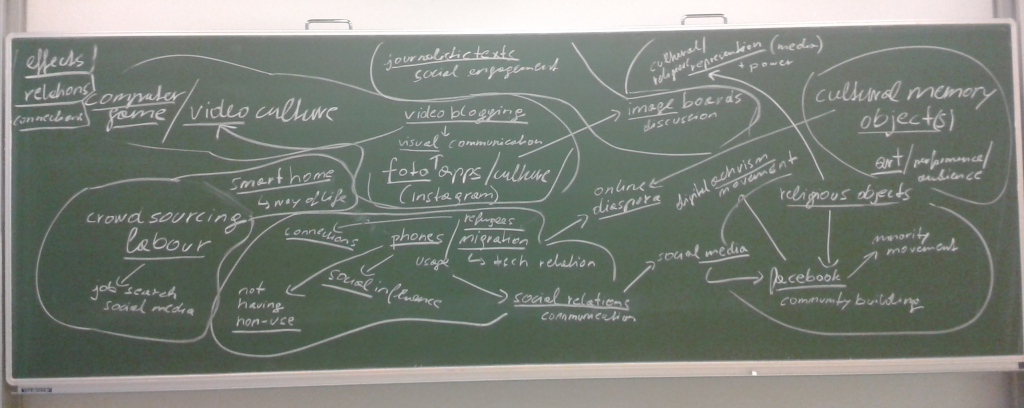
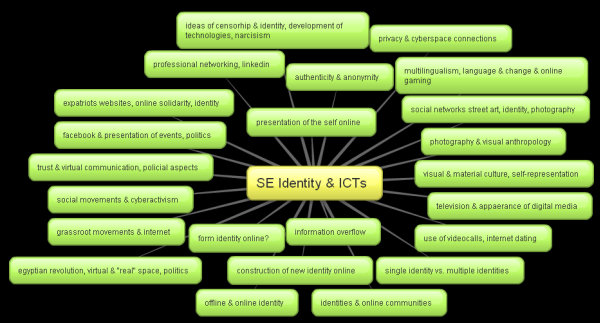
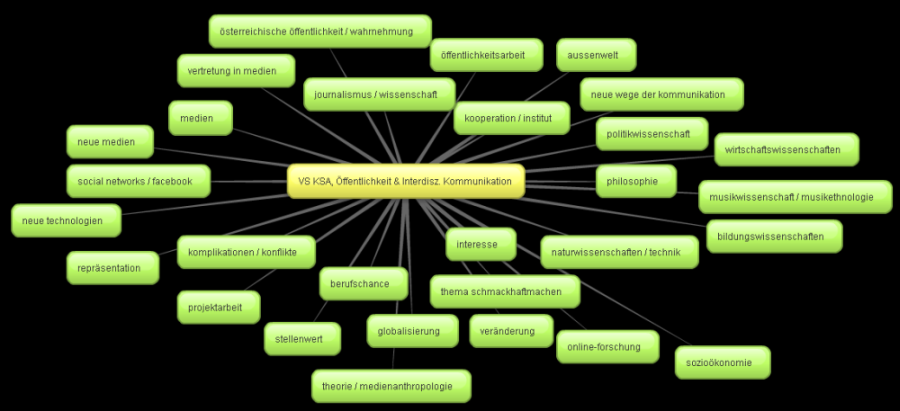
Dieser Vortrag wirft einen Blick auf die kultur- und sozialanthropologische Erforschung digitaler Medientechnologien wie Internet, Soziale Online-Netzwerke und mobile Kommunikationstechnologien. Dabei werden die Grundzüge des Forschungsfeldes der „Cyber Anthropologie“ – besonders im Bezug zum Wiener Institut für Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie – ebenso vorgestellt wie die rezente Entwicklung einer „Digitalen Anthropologie“. Die gemeinsame, übergeordnete Frage dieser kultur- und sozialanthropologischen Projekte lautet: „Was bedeutet Menschsein in einer (zunehmend) digitalen Welt?“. Fallbeispiele aus der ethnographischen Forschungspraxis behandeln konkrete Aspekte des „digitalen Menschseins“ und runden die theoretische Diskussion ab.
Medienanthropologie und die technische Mediatisierung von Kommunikation
In der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie lässt sich die Forschung zu Medientechnologien grundsätzlich als Forschung zu menschlicher Kommunikation, die von Technologien mediatisiert wird, verstehen. Diese Mediatisierung von Kommunikation ist für die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie besonders hinsichtlich ihrer Einbettung in soziokulturelle und historische Prozesse und Kontexte interessant: „The key questions for the anthropologist are how these technologies operate to mediate human communication, and how such mediation is embedded in broader social and historical processes“ (Peterson 2003: 5).
In der Medienanthropologie geht es um die Mediatisierung von Kommunikation in unterschiedlichen soziokulturellen Kontexten und unter spezifischen historischen, politischen und ökonomischen Bedingungen.
In der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie werden Medien nicht auf ihre Inhalte oder Botschaften reduziert. Im Versuch ein möglichst ganzheitliches Bild von Medienphänomenen zu erlangen, werden Kontexte und Bedingungen unter denen Medien produziert, verteilt und genutzt werden ebenso analysiert wie die technischen Aspekte von Medien. Medien beinhalten immer auch Technologien, die die Mediatisierung von Kommunikation erst ermöglichen. Es macht also Sinn nicht nur von Medien sondern von Medientechnologien zu sprechen.
Über Medientechnologien entwickeln Menschen neue Beziehungen zu Zeit und Raum sowie zu Körper und Wahrnehmung. Und diese Verhältnisse verändern sich aufgrund medientechnologischer Entwicklungen permanent. Die „greifbare“ Materialität von Medientechnologien und die damit verbundenen phänomenologischen Erfahrungen sind also wesentlicher Gegenstand medienethnographischer und medienanthropologischer Forschung (vgl. Ginsburg et al. 2002: 21).
Wichtigste methodische Herangehensweise, um Medienphänomene zu erfassen, ist für die Medienanthropologie, wie für die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie im Allgemeinen, die ethnographische Feldforschung. Diese methodische Strategie zur empirischen Datenerhebung passt sich dabei sowohl dem Feld als auch den soziokulturellen Handlungsräumen der Menschen an (vgl. z.B. Kremser 1998, Marcus 1998) und kann sich also nicht allein auf Inhalte und deren Rezeption beschränken. Sie muss auch die physischen und sensorischen Dimensionen von Medientechnologien miteinbeziehen, weil über diese soziale Beziehungen hergestellt werden können.
Technologie im soziokulturellen Kontext
Seit den 1950er Jahren untersuchen Kultur- und SozialanthropologInnen neue und „moderne“ Technologien und wie diese vor allem in „nicht-westlichen“ Gemeinschaften verwendet und angeeignet werden (vgl. z.B. Beck 2001, Godelier 1971, Pfaffenberger 1992, Sharp 1952). Doch wie unter anderem Arturo Escobar (1994) meint, ist es schwierig diese Forschungsansätze und -befunde auf hochkomplexe technische Umgebungen in „modernen“ Gesellschaften zu übertragen. Aus kultur- und sozialanthropologischer Perspektive bedeutet diese Transferschwierigkeit weder eine Hierarchisierung von soziotechnischen Systemen und damit verbunden von Gesellschaften, noch bedeutet dies eine Abwertung „nicht-moderner“ oder „traditioneller“ soziotechnischer Systeme. All diese Systeme – vom Töpfern in Indien bis zum Programmieren von Software in Kalifornien – sind hochkomplex und heterogen.
Es besteht allerdings dringender Bedarf an theoretischen Zugängen und weiteren empirischen Befunden, die zum Verständnis soziotechnischer Systeme in „modernen“ Gesellschaften beitragen. So befasst sich auch die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie zunehmend mit soziotechnischen Systemen in zeitgenössischen Gesellschaften (vgl. z.B. Rabinow 2008, Rabinow & Marcus 2008) – vor allem auch, weil immer wieder Fragen auftauchen, die scheinbar nur von der Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie beantwortet werden können, etwa nach der soziokulturellen und soziokulturell unterschiedlichen Bedeutung von Technologien (vgl. Pfaffenberger 1988, 1992).
Die Kultur- und Sozialanthropologie versucht zu verstehen, wie Technologie – beispielsweise in Form materieller Kultur oder als soziotechnisches System – (kulturell) konstruiert und (sozial) verwendet, genutzt und angeeignet wird. Ähnliche Ziele verfolgen auch Wissenschaftsforschung, Science and Technology Studies und sozialwissenschaftliche Technikforschung (vgl. z.B. Eglash 2006). Die Entwicklung und der Aufschwung digitaler (Medien)Technologien führen zu einer weiteren Differenzierung dieses Forschungsbereichs und zur Etablierung neuer Schwerpunkte.
Text (PDF)