The EASA Media Anthropology Network is organizing a panel entitled “Media anthropology’s legacies and concerns” at the 14th European Association of Social Anthropologists (EASA) conference in Milan (20-23 July, 2016). Please find the detailed call for papers below. To propose a paper, please navigate to http://nomadit.co.uk/easa/easa2016/panels.php5?PanelID=4286 and http://www.easaonline.org/conferences/easa2016/cfp.shtml
Deadline for paper proposal submissions is February 15th.
Media anthropology’s legacies and concerns
(Media Anthropology Network)
Convenors
Philipp Budka (University of Vienna)
John Postill (RMIT University Melbourne)
Elisenda Ardevol (UOC, Barcelona)
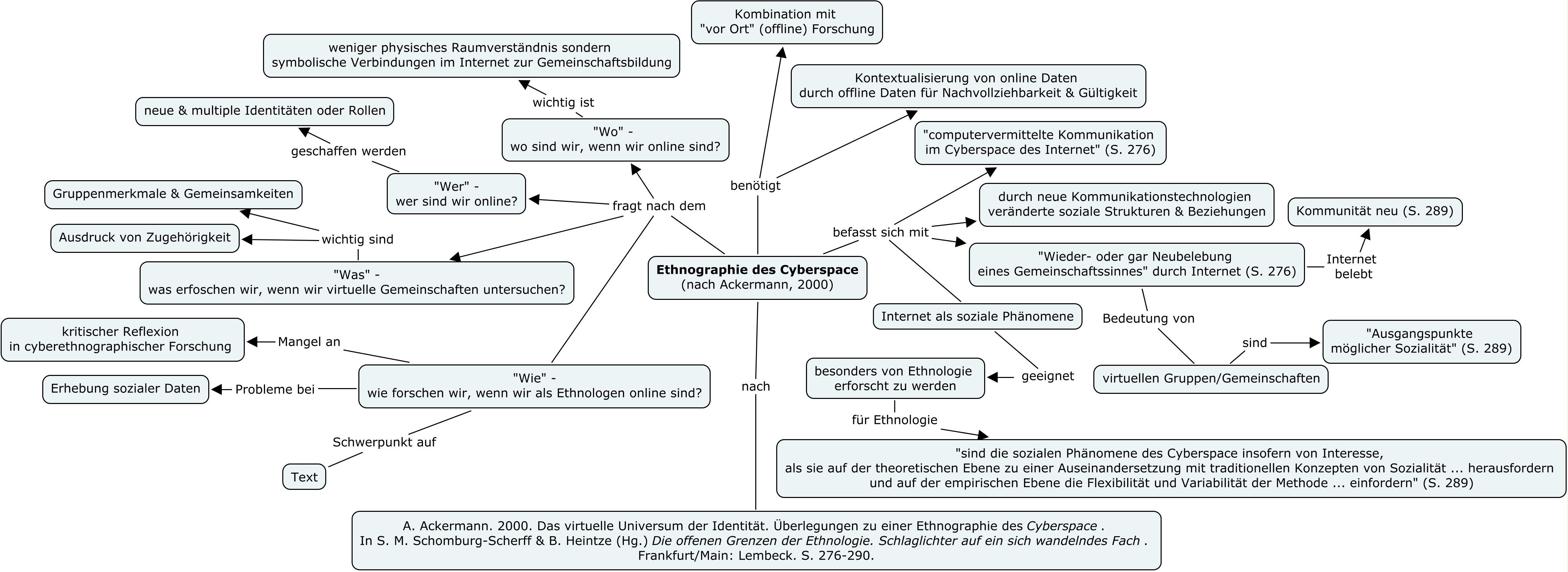
In line with the theme of the 14th EASA conference the EASA Media Anthropology Network panel seeks to put fundamental concerns of media anthropology back into the centre of attention. Central themes of media anthropology have already been identified and discussed in earlier works: e.g. the mediation of power and conflict, media related forms of production and consumption, the relationship between media and religion, and the mediation of knowledge and forms of expression (e.g. Askew & Wilk 2002, Ginsburg et al. 2002, Peterson 2003, Rothenbuhler & Coman 2005). These topics can be connected to questions about hierarchies, power relationships, norms and political agency in media contexts; the materiality of media (technologies), exchange and reciprocity, media work; media rituals and the ritualization of media practices and events; the construction of histories and traditions in relation to media practices and the meanings of media communication for oral culture(s).
By (re-)focusing on such topics in a contemporary context, this panel invites contributions also to discuss broader questions. What has been “the point of media anthropology” as an anthropological subdiscipline and as an interdisciplinary field of research (Postill & Peterson 2009)? What are media anthropology’s legacies so far and what are its historical roots? What role does ethnography play in the anthropology of media and how has this relationship changed from a methodological and epistemological perspective? Thus, this panel contributes to the constitution of media anthropology as one of anthropology’s most thriving subdisciplines. Secondly, it adds to the understanding of media anthropology’s legacies, epistemologies, theories, methodologies and possible futures.
Askew, K., Wilk, R. (eds.) 2002. The anthropology of media: A reader. Malden, MA: Blackwell.
Ginsburg, F., Abu-Lughod, L., Larkin, B. (eds.) 2002. Media worlds: Anthropology on new terrain. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Peterson, M. A. 2003. Anthropology and mass communication. Media and myth in the new millennium. New York & Oxford: Berghahn.
Postill, J., Peterson, M. A. 2009. What is the point of media anthropology? Social Anthropology 17(3): 334-344.
Rothenbuhler, E., Coman, M. (eds.) 2005. Media Anthropology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.